Gas
Laws explain the behavior of an ideal gas in terms of temperature, pressure,
volume.
The following are the some of the important gas laws:
The following are the some of the important gas laws:
- Boyle’s Law
- Charles Law
- Gay-Lussac’s Law
- Avogadro’s law
- Universal Gas Law
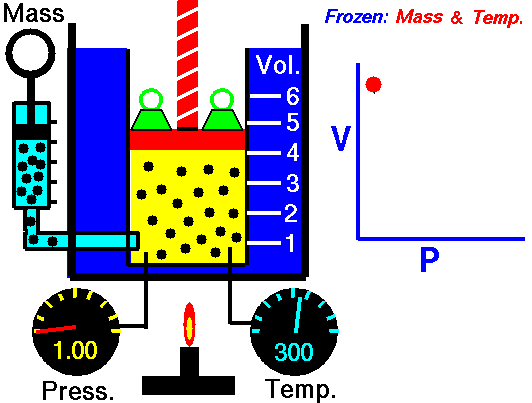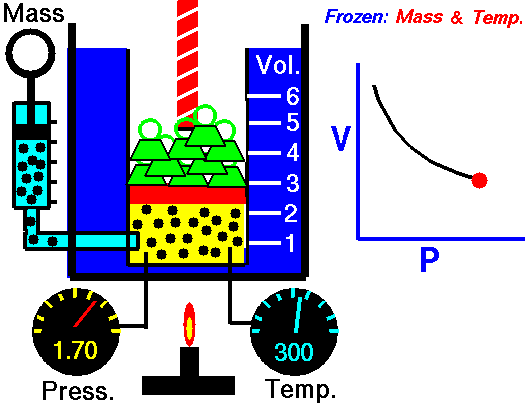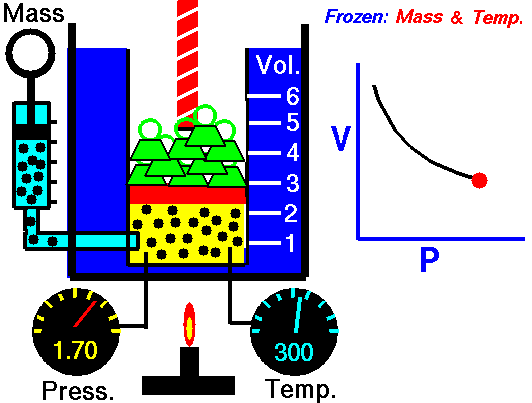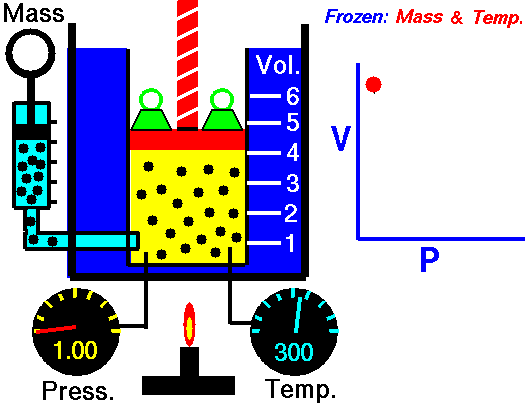
Boyle’s law states that the volume of a given mass of gas (V) is inversely proportional to its absolute pressure (P), provided the temperature of the gas (T) remains constant.
Boyle’s law formula

Charles Law:
According
to Charles law, the volume of a given mass of gas (V) is directly proportional
to its absolute temperature (T), when its pressure remains constant.
Gay-Lussac’s Law:
Gay-Lussac’s
Law is also know as Amontons’ law. It
states that if the volume of a given mass of a gas (V) is kept
constant, then the pressure of the gas (P) is
directly proportional to its absolute temperature (T).
Gay-Lussac’s
Law Formula:

Avogadro’s Law:

Avogadro’s Law:
Avogadro’s law states that equal volumes of different perfect
gases, at the same temperature (T) and
pressure (P),
contain equal number of molecules (n).
Avogadro’s law equation


Universal Gas Law:
Combined Gas law is derived from the three gas
laws Boyle's law, Charles law and Gay-Lussacs law.
Universal Gas Law Formula