The
milling is a machining process in which, a rotary cutter is used to
remove the material from work piece in the direction perpendicular to
the axis of rotation. The
milling process is done by the machine, which hold both the tool and
work piece in jig and fixture, known as milling machine. There
are two ways to cut the material from the work piece through milling
machine. First one is named as conventional milling or Up milling and
the other one known as climb milling or down milling. The main and basic
difference between up milling and down milling is the direction of
rotation of cutter to the feed.
The milling operation is used to face those work piece, which are not symmetrical from its axis. It is also used to cut pockets, drill, slot and shape the work piece according to the requirement.
The milling operation is used to face those work piece, which are not symmetrical from its axis. It is also used to cut pockets, drill, slot and shape the work piece according to the requirement.
There
are two ways to cut the material from the work piece through milling
machine. First one is named as conventional milling or Up milling and
the other one known as climb milling or down milling. The main and basic
difference between up milling and down milling is the direction of
rotation of cutter to the feed.
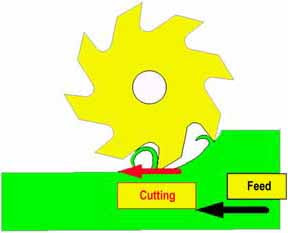
In
up milling the cutter rotates clockwise when cutting the work piece
from right to left. In this type of milling the tool spins against the
direction of feed. In this milling process, the cutting chips are
carried upward by the tool.
|
Up Milling
|
Down Milling
|
|
In up milling the cutter rotates against
direction of feed.
|
In Down milling, the cutter rotates with
direction of feed.
|
|
It is also known as conventional milling.
|
It is also known as climb milling.
|
|
In this, chip width size is zero at initial
cut and increase with feed. It is maximum at the end of feed.
|
In this cutting process, chip size is maximum
at start of cut and decrease with the feed. It is zero at the end of feed.
|
|
In this process, heat is diffuse to the work
piece which causes the change in metal properties.
|
In down milling most of heat diffuse to the
chip does not change the work piece properties.
|
|
In up milling, tool wear is more because the
tool runs against the feed.
|
In this, tool wear is less compare to the up
milling, due to the cutter rotate with the feed.
|
|
Tool life is low.
|
Tool life is high.
|
|
The cutting chips are carried upward by the
tool so known as up milling.
|
The chips are carried downward by the tool so
known as down milling.
|
|
The cutting chips fall down in front of the
cutting tool which again cut the chips cause less surface finish.
|
The cutting chips fall down behind the tool.
This gives better surface finish.
|
|
Due to upward force by tool, high strength
zig and fixture required to hold the work piece.
|
In down milling, downward force act on work
piece normal zig and fixture required.
|
|
|
|